Coeliac Disease – What you need to know
Please note, this page is printable by selecting the normal print options on your computer.
What is Coeliac disease?
Coeliac disease is a life-long condition. People who have it, cannot tolerate a specific protein called gluten. Gluten is found in wheat, barley and rye and in foods made from these grains.
• Approximately one person in every 100 is likely to have Coeliac disease.
• The disease can be diagnosed at any age.
• The most common age of diagnosis is 40-50.
What happens if you suffer from coeliac disease and eat gluten?
Lining the gut (small intestine) are tiny, finger-like projections called villi. In Coeliac disease gluten causes these to become inflamed and flattened. This is called villous atrophy and it makes the gut unable to absorb nutrients from food. It also causes a variety of other symptoms such as diarrhoea, abdominal discomfort, fatigue, anaemia and weight loss. Coeliac disease cannot be cured but it can be managed effectively by following a strict gluten-free diet, which is continued for life.
A Gluten-free diet
Gluten is found in wheat, barley and rye, and so foods made with these grains should be avoided. Some manufactured foods also contain small amounts of gluten. This will be stated on the ingredients list or the food packaging. Additionally, Coeliac UK publish an annual Food and Drink Directory which lists manufactured foods that are gluten free.
What about oats?
Oats contain a similar protein to gluten, which are called avenins. Most people with Coeliac disease can tolerate a small amount of oats in the diet; however, it is advisable to wait until your coeliac disease is under control (i.e. symptom free). If you wish to include oats into your diet, please discuss this with your Dietitian, Gastroenterologist or GP first to enable them to offer suitable advice and supervision to rule out intolerance to them. Please also ensure you check that the oats are labelled gluten free before you eat them.
Shopping check list
• Always check ingredients lists on foods, to see whether the product contains gluten
• Foods or drinks which cause allergy may have a special allergen advice box on the label e.g. “Contains: gluten, milk and nuts”. However not all manufacturers do this, therefore it is helpful to check ingredients lists
• When the crossed grain symbol appears on packaging it means the food is guaranteed to be gluten-free. The symbol is owned by Coeliac UK and is used under licence by food producers
Reading Food Labels
If the following words appear in the ingredients list, it means the food is not glutenfree: Wheat starch, Malt, Modified wheat starch, Barley flour, Rye (unless there is an allergen box which says gluten-free). The following ingredients do not contain gluten: Maize starch, Maltitol, Isomalt, Xantham gum, Modified maize starch, Textured vegetable protein, Malto-dextrin, Caramel, Glucose syrup, Artificial sweetener, Sorbitol, Aspartame, Dextrose.
Codex wheat starch – means the gluten has been removed to a safe level and is safe to eat despite containing wheat.
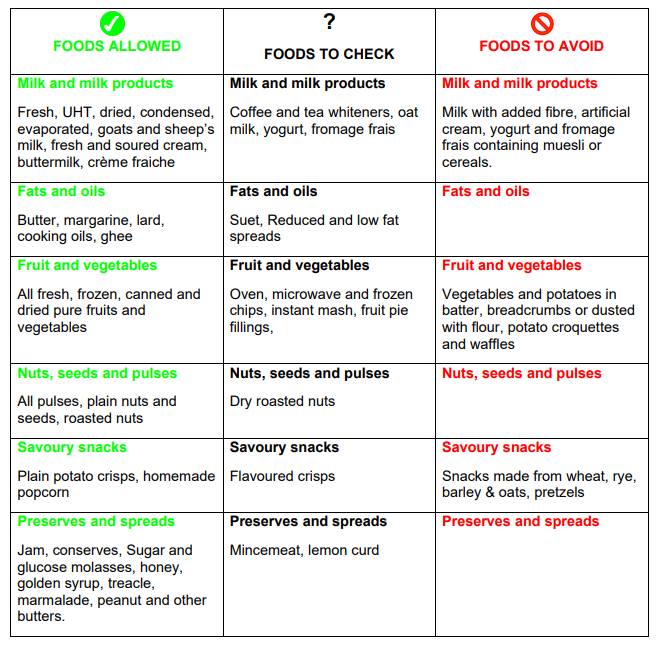
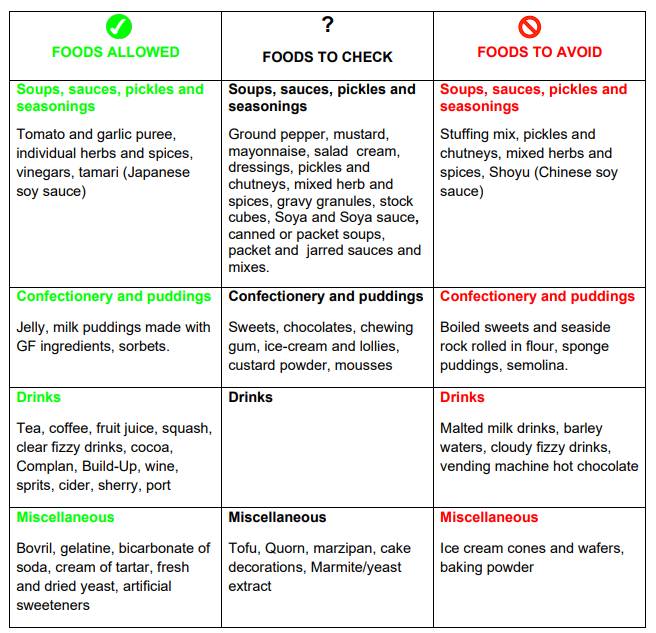
Gluten Free check list
The following pages list basic foods that are allowed, need to be checked or should be avoided completely. You should also use Coeliac UK’s Food List to check manufactured food products.
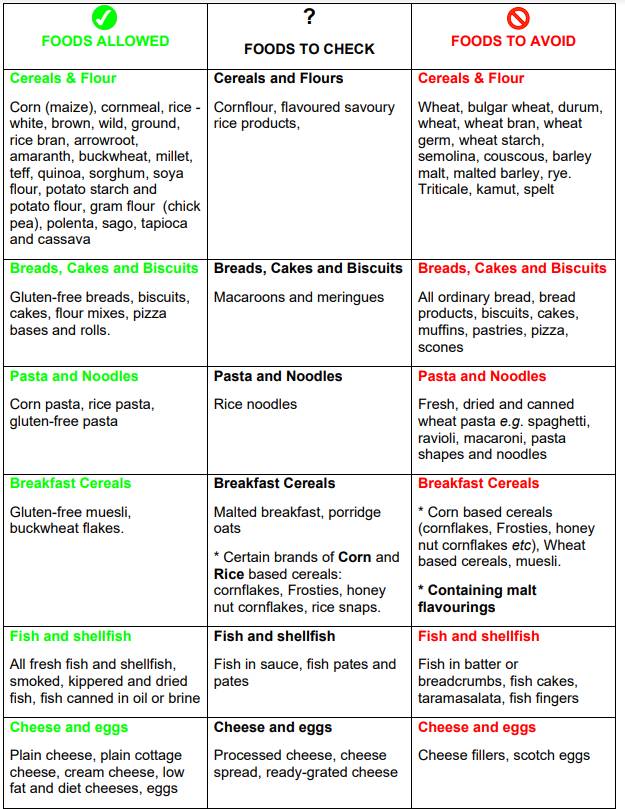
* Barley malt extract in low levels that meet Codex standards can be tolerated by most people
with coeliac disease. If it is listed in the Coeliac UK Food and Drink Directory it is safe to have.
More Information: Coeliac UK
Coeliac UK is the charity that supports patients who have been diagnosed with Coeliac disease. The charity can provide recipe idea, eating out guidance as well as information on all foods and drinks that are gluten free from a range of supermarkets. To become a member of Coeliac UK, please contact them using one of the following contact routes:
Coeliac UK Office: 3rd Floor, Apollo Centre, Desborough Road, High Wycombe, Buckinghamshire.
0845 305 2060 www.coeliac.org.uk
